Geographic tongue, also known as benign migratory glossitis, is a relatively harmless yet curious condition that affects the appearance of the tongue. Its name derives from the way the tongue’s surface develops map-like patches of discoloration or smooth areas, much like the shifting patterns of a geographic map. Though the condition is not typically dangerous, it can cause discomfort or anxiety for those affected.
What Is Geographic Tongue?
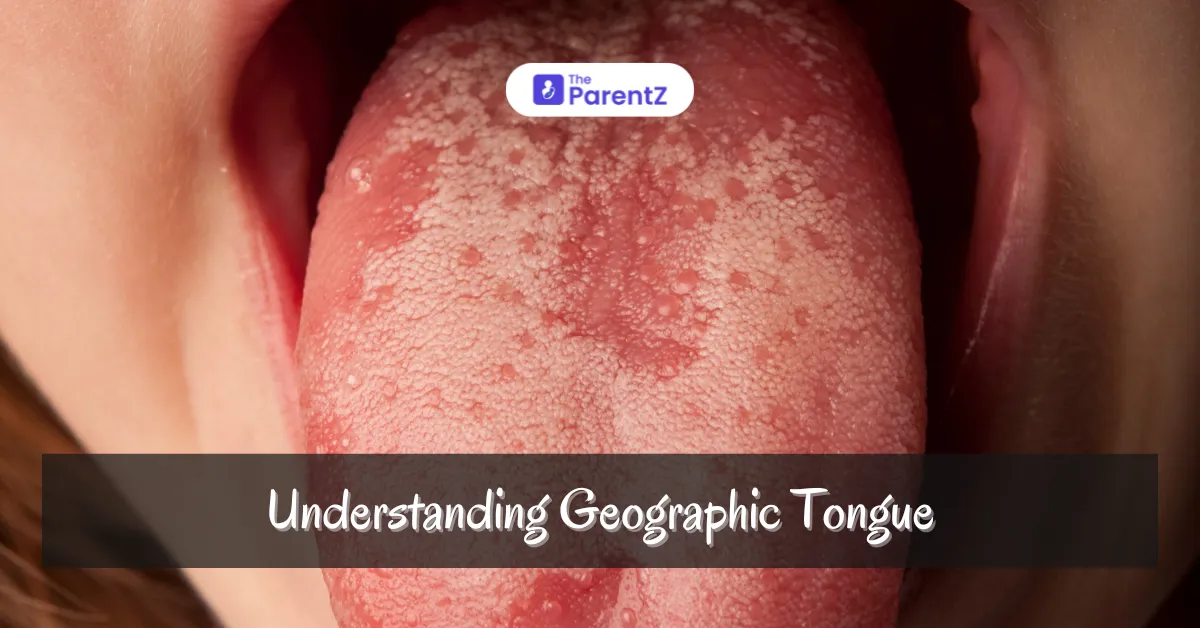
Geographic tongue is a condition where patches of the tongue lose their tiny bumps known as papillae, creating smooth, red areas that often change shape and location over time. These areas can be bordered by white or gray lines, making the pattern look somewhat like a map, hence the name.
This condition is classified as benign because it usually doesn’t lead to serious health issues, and it is not contagious or cancerous. However, geographic tongue can cause sensitivity, particularly when consuming certain foods.
Symptoms of Geographic Tongue
While geographic tongue is often painless, there are cases where it can cause sensitivity or discomfort, especially when exposed to hot, spicy, or acidic foods. The key symptoms to watch for include:
1.Smooth, Red Patches on the Tongue
The most noticeable symptom is the presence of smooth, reddish patches on the surface of the tongue. These patches often have slightly raised white or light-colored borders. The patches can vary in size and shape, sometimes changing location from one part of the tongue to another over time.
2.Changing Appearance
One of the most distinctive features of geographic tongue is that it is migratory. The patches can shift in position, disappearing from one area and reappearing in another, often within days. This shifting nature can make it more puzzling and concerning for those who are unfamiliar with the condition.
3.Sensitivity to Foods
Some individuals with geographic tongue experience increased sensitivity, especially to foods that are spicy, hot, or acidic. This sensitivity can cause discomfort or a burning sensation when eating certain items like citrus fruits, tomatoes, or hot peppers.
4.Mild Discomfort or Irritation
In some cases, people may feel a slight burning or tingling sensation, though this is generally mild and temporary. Geographic tongue is not usually associated with significant pain or other serious symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of geographic tongue is not well understood, but several factors have been linked to its development. It’s believed that the condition may be related to a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune factors.
1. Genetic Predisposition
There is evidence to suggest that geographic tongue may run in families, indicating a potential genetic component. If someone in your family has experienced this condition, you may be more likely to develop it as well.
2. Immune System Factors
Geographic tongue has been observed more frequently in individuals with immune system-related conditions like psoriasis. Some experts believe that an overactive immune response may play a role in the development of the condition, though this is not yet fully understood.
3. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations have been suggested as a potential trigger for geographic tongue, especially in women. Some studies have linked the condition to times of hormonal change, such as during pregnancy or menopause.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies
Though not a primary cause, some cases of geographic tongue have been associated with deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as vitamin B12, iron, or zinc. Ensuring a well-balanced diet may help prevent or alleviate the symptoms in some individuals.
Diagnosis of Geographic Tongue
Diagnosing geographic tongue is typically straightforward. Dentists and doctors can usually identify the condition based on the appearance of the tongue alone. In rare cases, a biopsy or other diagnostic tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms, such as infections or more serious diseases like oral cancer.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you notice changes in the appearance of your tongue, especially if they are accompanied by persistent discomfort, swelling, or sores that don’t heal.
How to Manage Geographic Tongue
Though geographic tongue does not usually require treatment, managing the condition focuses on reducing discomfort and avoiding triggers that can cause irritation.
1. Avoid Irritating Foods
To minimize sensitivity, it’s a good idea to avoid foods that commonly trigger discomfort. These include hot, spicy, acidic, and salty foods. Items like citrus fruits, tomatoes, and spicy dishes can exacerbate sensitivity, so consider reducing or eliminating them from your diet if they cause issues.
2. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Keeping your mouth clean can help prevent additional irritation. Regular brushing, flossing, and using a mild mouthwash can reduce the risk of bacterial buildup, which might worsen symptoms. Be sure to use a toothpaste that is free from harsh ingredients like sodium lauryl sulfate, which can sometimes irritate sensitive mouths.
3. Stay Hydrated
Dryness in the mouth can increase irritation, so staying hydrated is crucial. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help keep your mouth moist and reduce discomfort.
4. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
In cases of significant discomfort, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be helpful. These medications can help alleviate any mild pain or irritation caused by geographic tongue.
5. Topical Gels or Mouth Rinses
Some individuals may find relief by using topical gels or prescribed mouth rinses designed to soothe oral discomfort. Consult your dentist or doctor if you feel these treatments could benefit you.
When to See a Doctor
While geographic tongue is usually harmless, there are times when a visit to the doctor or dentist is necessary. Seek medical attention if you experience:
•Persistent sores that do not heal
•Significant swelling or pain
•Changes in the tongue’s appearance that last for more than a few weeks
•Difficulty eating, speaking, or swallowing
These could be signs of a more serious condition that requires prompt medical attention.
Conclusion
Geographic tongue may be visually alarming, but it is generally a benign condition that poses no serious threat to your health. While it can cause some discomfort and sensitivity, these symptoms are typically manageable with a few lifestyle adjustments and good oral hygiene.







Be the first one to comment on this story.