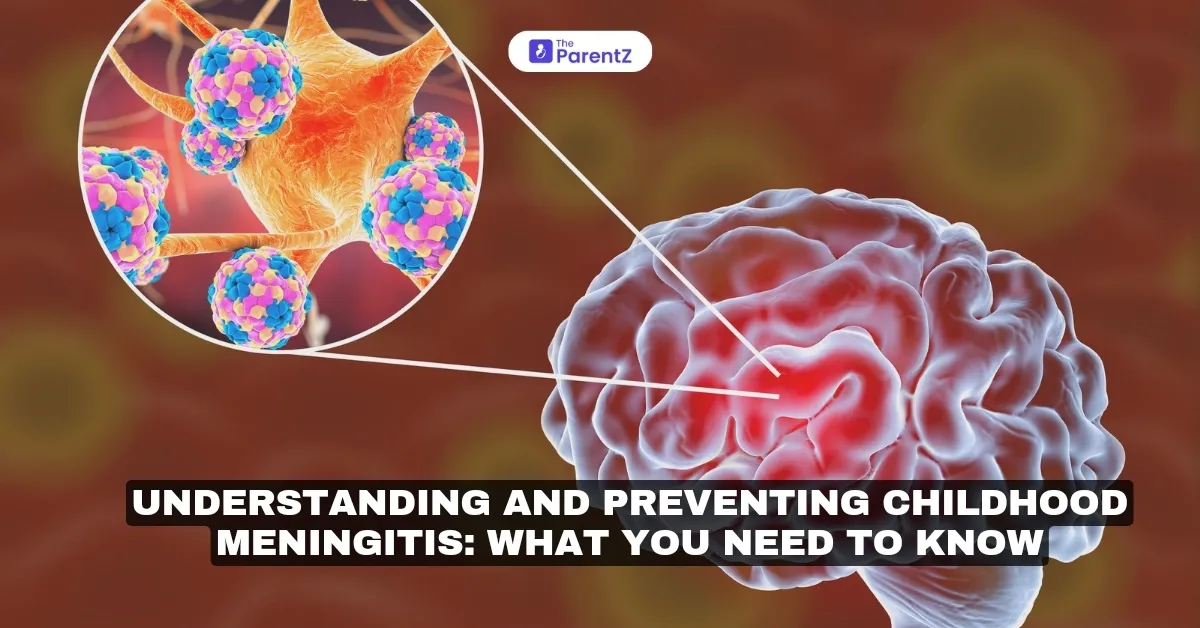
Meningitis in kids is a life-threatening condition and it refers to the inflammation of the membranes (meninges) surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is typically caused by an infection and can lead to permanent neurological damage, hearing loss, or even death if left untreated.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), bacterial meningitis affects over 2.5 million people globally each year. In the U.S. alone, nearly 1000–2600 people suffer from bacterial meningitis every year, with 10 percent of cases resulting in death, as per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Furthermore, children under five are at the highest risk.
Read this article to learn about meningitis in kids, its causes, symptoms, and treatment.
Causes of Childhood Meningitis
Depending on the type of meningitis, the causes may vary. Here are the causes of different types of meningitis in kids.
Bacterial Meningitis
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), bacterial meningitis is more prevalent in infants, toddlers, and adolescents. It is the most complicated and serious form, and the common causes for bacterial meningitis in kids include
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus)
- Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus)
- Haemophilus influenzae type B
Viral Meningitis
Viral meningitis is typically less severe than bacterial meningitis and often cures on its own. It is caused by enteroviruses, such as coxsackievirus and echovirus.
Fungal and Parasitic Meningitis
Fungal/parasitic meningitis is a rare condition and typically affects children with weakened immune systems. It is primarily caused by Cryptococci, and kids with immunodeficiency concerns are at a higher risk.
Symptoms of Meningitis in Kids
There is a rapid progression in the symptoms of meningitis in kids. The common signs of meningitis in kids include
In Infants
- Fever
- Poor feeding
- Vomiting
- Irritability or lethargy
- Soft spot on the baby’s head
In Older Kids
- Severe headache
- High fever
- Neck stiffness
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty concentrating
- Seizures
Prevention Tips for Childhood Meningitis
Vaccines are an effective way to prevent childhood meningitis. Some of the essential vaccines that prevent meningitis include
Hib Vaccine
According to the CDC, this vaccine must be administered to infants starting at two months of age. It protects against Haemophilus influenzae type b, which is considered one of the leading causes of bacterial meningitis.
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
PCV13 is an effective vaccine that protects against Streptococcus pneumoniae, a common cause of bacterial meningitis. It is routinely administered to infants and children under five.
Meningococcal Vaccine
The meningococcal conjugate vaccine is recommended for children at 11–12 years old, with a booster at 16. Besides, a separate vaccine for meningococcal B (MenB) is also recommended for teens and young adults.
Treatment
The treatment for meningitis in children depends on the cause. For bacterial meningitis, your healthcare provider may recommend immediate hospitalization, including IV antibiotics, since delayed treatment may lead to brain damage, hearing impairment, and even death.
Viral meningitis, however, is less severe and cures without specific treatment. Although prompt treatment may be required for children with extremely weakened immune systems, if the children suffer from fungal meningitis, kids with weak immune systems require antifungal medications and hospitalization depending on the severity.
Takeaway
Childhood meningitis is a serious condition that needs immediate medical attention to avoid severe outcomes. The best way to prevent meningitis in kids is vaccination and practicing good hygiene habits, as it can significantly reduce the risk of viral infections. If you suspect any signs of meningitis in your kids, they seem to require immediate medical attention.






Be the first one to comment on this story.