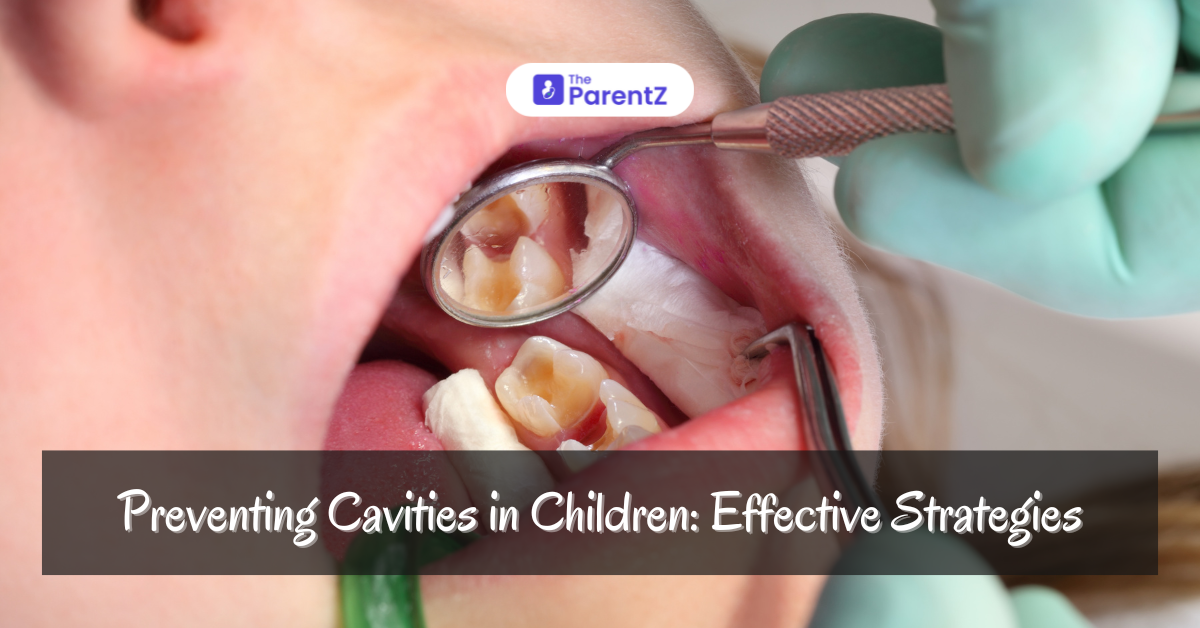
What Are Cavities?
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are permanently damaged areas in the hard surface of your teeth that develop into tiny openings or holes. They are caused by a combination of factors, including bacteria in the mouth, frequent snacking, sipping sugary drinks, and not cleaning your teeth well. Cavities are one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood and, if left untreated, can lead to pain, infection, and even loss of teeth.
How Cavities Affect Children’s Health
1. Pain and Discomfort: Cavities can cause significant pain and discomfort, making it difficult for children to eat, speak, and focus on daily activities.
2. Infection: Untreated cavities can lead to tooth abscesses and infections that can spread to other parts of the body.
3. Difficulty Eating: Pain from cavities can make it hard for children to chew food properly, leading to poor nutrition and growth problems.
4. Speech Development Issues: Cavities in the front teeth can affect a child’s ability to speak clearly.
5. School Absence: Dental problems are a common cause of missed school days and can affect a child’s academic performance.
6. Self-Esteem Issues: Visible cavities and damaged teeth can affect a child’s confidence and willingness to smile.
Common Types of Cavities in Kids
1. Pit and Fissure Cavities: These occur on the chewing surfaces of the back teeth where food particles are most likely to get stuck.
2. Smooth Surface Cavities: These develop on the smooth sides of the teeth and are slower to form but can spread quickly.
3. Root Cavities: Although more common in adults, children can develop root cavities if their gums recede due to poor oral hygiene.
4. Interproximal Cavities: These cavities form between the teeth and are often detected through dental X-rays.
How to Prevent Cavities in Kids
1. Good Oral Hygiene Practices:
– Brush teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
– Use an age-appropriate toothbrush with soft bristles.
– Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth.
– Supervise young children while brushing to ensure they do it properly.
2. Healthy Diet:
– Limit sugary and starchy foods and drinks.
– Encourage a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products.
– Provide water as the main drink and avoid sugary drinks.
3. Regular Dental Checkups:
– Schedule dental visits every six months for professional cleanings and checkups.
– Discuss fluoride treatments and dental sealants with your dentist.
4. Fluoride Use:
– Use fluoride toothpaste and consider fluoride supplements if recommended by your dentist.
– Drink fluoridated water if available.
5. Dental Sealants:
– Dental sealants are thin, protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of the back teeth to prevent cavities.
– Sealants can reduce the risk of decay by nearly 80% in molars.
6. Avoid Prolonged Bottle Feeding:
– Avoid putting your child to bed with a bottle, as prolonged exposure to milk or juice can lead to tooth decay.
– Transition from bottle to cup by the age of 1 year.
Treatment Modalities for Cavities in Kids
1. Fluoride Treatments: Professional fluoride treatments can help reverse early decay and strengthen teeth.
2. Dental Fillings: Cavities are cleaned and filled with materials such as composite resin, amalgam, or glass ionomer.
3. Crowns: For extensive decay, especially in baby teeth, crowns may be used to restore function and appearance.
4. Pulpotomy: For cavities that reach the pulp of the tooth, a pulpotomy may be performed to remove the infected tissue and preserve the remaining tooth.
5. Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, it may need to be extracted to prevent further infection and damage.
Conclusion
Preventing cavities in children requires a combination of good oral hygiene, a healthy diet, regular dental visits, and preventive treatments like fluoride and sealants. By instilling these habits early, parents can help their children maintain healthy, cavity-free teeth and avoid the pain and complications associated with dental decay. Regular communication with a pediatric dentist ensures that any issues are detected and treated promptly, promoting overall dental health and well-being for your child.






Be the first one to comment on this story.