Gallbladder issues during pregnancy, such as gallstones or inflammation, can complicate an already delicate period. Hormonal changes, dietary habits, and the physical pressure of the growing uterus can contribute to gallbladder problems.
What Causes Gallbladder Issues During Pregnancy?
Pregnancy increases the risk of gallbladder problems due to hormonal and physical changes, including:
1. Hormonal Changes
• Elevated levels of progesterone during pregnancy slow the emptying of the gallbladder, leading to bile stasis.
• This can increase the likelihood of gallstone formation.
2. Dietary Factors
• High-fat diets can exacerbate gallbladder problems by overstimulating bile production.
• Limited physical activity may also contribute to bile stagnation.
3. Uterine Pressure
• The growing uterus can compress the gallbladder, impairing its function and exacerbating preexisting issues.
Common Gallbladder Issues During Pregnancy
1. Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)
• Hardened deposits of bile that can block the bile ducts.
• Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, upper abdominal pain (especially after fatty meals), and jaundice.
2. Inflammation (Cholecystitis)
• Inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by gallstones.
• Symptoms: Severe pain in the right upper abdomen, fever, and tenderness.
3. Biliary Sludge
• A mixture of bile and particles that can form before gallstones.
• Symptoms: May cause mild discomfort or remain asymptomatic.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Problems During Pregnancy
• Sharp pain in the upper right abdomen (radiating to the back or shoulder).
• Nausea and vomiting.
• Indigestion or bloating, especially after high-fat meals.
• Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
• Fever or chills (in cases of inflammation).
Diagnosis of Gallbladder Issues
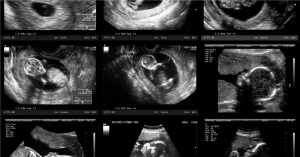
• Ultrasound: The most common and safe imaging method during pregnancy to detect gallstones or inflammation.
• Blood Tests: Used to identify signs of infection, liver dysfunction, or bile obstruction.
• Physical Examination: To check for tenderness in the upper right abdomen.
Managing Gallbladder Issues During Pregnancy
1. Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications
• Opt for a low-fat diet: Avoid fried or greasy foods to reduce stress on the gallbladder.
• Eat smaller, frequent meals to improve digestion and prevent bile buildup.
• Stay hydrated and include fiber-rich foods to aid in digestion.
2. Medications
• Pain relief: Acetaminophen is commonly recommended, but always consult your doctor before taking medications.
• Bile acids may be prescribed to dissolve small gallstones.
3. Surgery (Cholecystectomy)
• In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the gallbladder.
• Laparoscopic surgery is considered safe during the second trimester, but the risks and benefits should be carefully assessed.
Potential Complications of Untreated Gallbladder Issues
• Preterm Labor: Severe pain or infection can increase the risk of preterm delivery.
• Infections: Untreated inflammation can lead to life-threatening infections such as sepsis.
• Pancreatitis: Gallstones can obstruct the bile ducts, leading to inflammation of the pancreas.
Preventing Gallbladder Problems During Pregnancy
• Maintain a Balanced Diet: Limit high-fat foods and focus on lean proteins, whole grains, and fresh vegetables.
• Stay Active: Regular light exercise can help prevent bile stasis.
• Monitor Weight Gain: Avoid excessive weight gain, as it increases the risk of gallstone formation.
Key Points
• Pregnancy increases the risk of gallbladder issues due to hormonal changes and bile stasis.
• Symptoms include upper right abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice.
• Gallstones and inflammation are the most common issues, with ultrasound being the primary diagnostic tool.
• Management includes dietary changes, medications, and in severe cases, surgery.
• Preventing complications requires a healthy lifestyle and regular monitoring.
Final Note
If you experience symptoms of gallbladder issues during pregnancy, consult your healthcare provider immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy for both mother and baby.