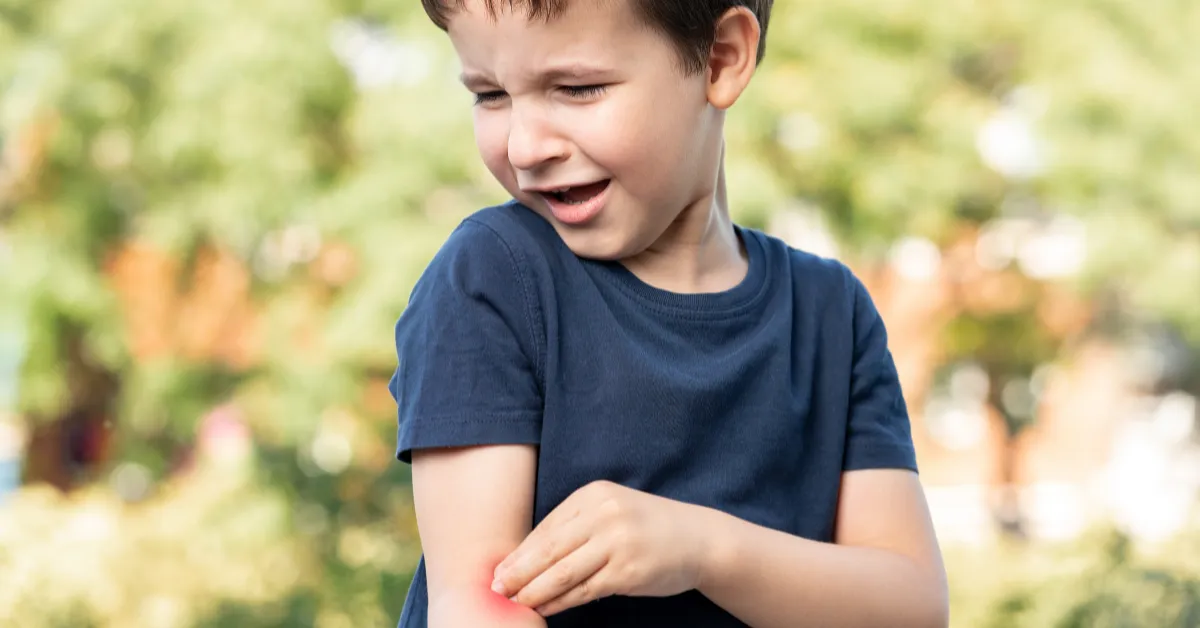
Children love to explore the outdoors, but this curiosity often exposes them to insect bites and stings. While most insect bites cause mild reactions like itching and redness, some can lead to severe allergic responses or infections. As a parent, knowing how to recognize and manage insect bites is crucial for your child’s safety.
Common Insects That Bite or Sting
Different insects can cause reactions ranging from mild discomfort to serious allergic reactions. Some of the most common culprits include:
1. Mosquitoes – Cause red, itchy welts and can transmit diseases like dengue and malaria.
2. Bees and Wasps – Stings can be painful and may trigger allergic reactions.
3. Ants (Fire Ants) – Bites cause burning pain, swelling, and pustules.
4. Spiders – Some, like the Black Widow or Brown Recluse, can cause serious symptoms.
5. Ticks – Can transmit Lyme disease and other infections.
6. Fleas – Often cause itchy red bumps, especially in warm areas.
7. Bedbugs – Leave small, red, itchy bites, often in clusters.
Understanding the insect involved can help determine the right course of action.
Recognizing an Insect Bite or Sting
Most insect bites cause localized symptoms such as:
• Redness and swelling at the site
• Itching or burning sensation
• Pain or tenderness
• Small, raised bumps or blisters
However, some bites can cause severe reactions requiring immediate medical attention.
When to Seek Medical Help
Seek emergency care if your child shows any of the following signs:
• Difficulty breathing or wheezing
• Swelling of the face, lips, or throat
• Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), including dizziness or fainting
• Rapid heartbeat or nausea
• A spreading rash or fever (possible infection)
First-Aid Measures for Insect Bites and Stings
1. General First-Aid Steps for All Bites & Stings
• Wash the area with soap and water to prevent infection.
• Apply a cold compress (ice wrapped in cloth) for swelling and pain.
• Use anti-itch creams or calamine lotion to reduce irritation.
• Monitor for allergic reactions, especially if it’s a first-time sting.
2. Specific Treatment for Different Insect Bites
Mosquito Bites
• Apply calamine lotion or antihistamine cream to relieve itching.
• Avoid scratching, as it can lead to infection.
• Use insect repellents when outdoors to prevent bites.
Bee and Wasp Stings
• Remove the stinger (if visible) using the edge of a credit card or tweezers.
• Apply a baking soda paste (1 part water, 3 parts baking soda) to neutralize venom.
• Give an oral antihistamine (if recommended by a doctor) for swelling or itching.
Ant Bites (Fire Ants)
• Clean the area with soap and water.
• Apply hydrocortisone cream to reduce swelling.
• Avoid popping blisters to prevent secondary infection.
Spider Bites
• For non-venomous spiders, clean the bite and apply an ice pack.
• For venomous spider bites (like the Black Widow or Brown Recluse):
• Seek medical attention immediately.
• Keep the bitten limb immobilized to slow venom spread.
• Monitor for symptoms like muscle pain, fever, or ulcer formation.
Tick Bites
• Use fine-tipped tweezers to remove the tick completely.
• Clean the bite with antiseptic.
• Watch for rash or flu-like symptoms (could indicate Lyme disease).
To learn more about venomous insect bites and their effects, you can check this article on venom toxicity.
Preventing Insect Bites and Stings
Prevention is always better than cure. Here’s how to reduce the risk of insect bites in children:
At Home
✔ Keep windows and doors closed or screened to prevent insects from entering.
✔ Remove standing water where mosquitoes breed.
✔ Regularly clean bedding and carpets to avoid bedbugs and fleas.
✔ Store food properly to prevent attracting ants and wasps.
Outdoors
✔ Dress children in light-colored, long-sleeved clothing when in insect-prone areas.
✔ Avoid strong perfumes or scented lotions, as they attract bees.
✔ Teach kids not to disturb ant hills, beehives, or spider webs.
✔ Use child-safe insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or natural oils like lemon eucalyptus.
If you’re interested in more first-aid tips for different insect stings, check out this article on emergency care.
Common Myths About Insect Bites
🚫 “All insect bites are harmless” – Some can lead to serious allergic reactions.
🚫 “Scratching helps heal the bite” – It actually increases the risk of infection.
🚫 “Applying butter or toothpaste on a sting works” – These can worsen irritation.
Always follow medical advice instead of relying on traditional remedies.
Conclusion
Insect bites and stings are common in children but can be effectively managed with prompt first aid and preventive measures. Parents must be aware of signs of allergic reactions, ensure proper hygiene, and teach children safety tips to reduce risks. If a bite seems severe, never hesitate to seek medical help.
By staying vigilant and prepared, you can ensure your child’s outdoor adventures remain safe and enjoyable.