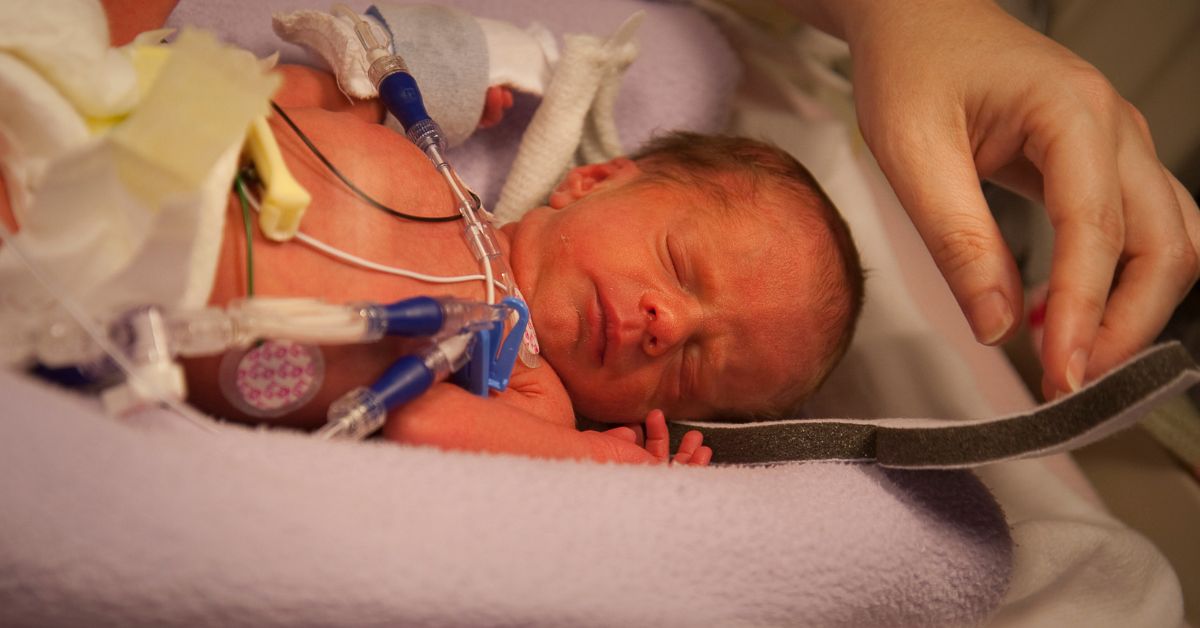
Caring for premature babies, or preemies, requires special attention and care due to their early arrival and the associated health challenges. Premature birth, defined as delivery before 37 weeks of gestation, can lead to various medical complications and developmental concerns. This article provides a comprehensive guide on the special considerations for caring for preemies, covering their unique needs, medical care, developmental support, and parental guidance.
In this article:
Introduction to Preemies
Premature birth occurs in about 10% of pregnancies worldwide. Preemies are categorized based on their gestational age at birth:
- Late Preterm: Born between 34 and 36 weeks.
- Moderately Preterm: Born between 32 and 34 weeks.
- Very Preterm: Born before 32 weeks.
These babies often face numerous health challenges due to underdeveloped organs and systems, requiring specialized medical care and developmental support.
Medical Challenges and Care
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)
Most preemies spend time in the NICU, where they receive specialized care to address their immediate health needs. The NICU provides:
- Incubators: To maintain a stable body temperature.
- Respiratory Support: Ventilators or CPAP machines to assist with breathing.
- Feeding Tubes: For nutrition if the baby cannot feed by mouth.
- Monitors: To track vital signs such as heart rate, oxygen levels, and blood pressure.
Common Medical Issues
Preemies are susceptible to several medical conditions, including:
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS): Caused by underdeveloped lungs, requiring respiratory support.
- Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH): Bleeding in the brain, which can lead to long-term neurological issues.
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC): A serious intestinal condition.
- Jaundice: High levels of bilirubin in the blood, leading to yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Anemia: A lower than normal number of red blood cells.
Nutritional Needs
Proper nutrition is critical for the growth and development of preemies. Key considerations include:
- Breast Milk: Provides essential nutrients and antibodies. Fortified breast milk or specialized preemie formulas may be recommended.
- Feeding Methods: Initially, tube feeding is common, transitioning to katori and spoon followed by bottle or breastfeeding as the baby grows stronger.
- Frequent Feeding: Preemies need small, frequent feedings to support their growth.
Developmental Support
Physical Development
Supporting the physical development of preemies involves:
- Physical Therapy: To enhance muscle strength and motor skills.
- Occupational Therapy: To assist with feeding, sensory integration, and fine motor skills.
- Positioning: Proper positioning in the incubator and during sleep to promote muscle development and prevent deformities.
Cognitive and Emotional Development
Cognitive and emotional support is crucial for preemies:
- Early Intervention Programs: Provide specialized support for developmental delays.
- Kangaroo Care: Skin-to-skin contact with parents helps regulate the baby’s body temperature, improves bonding, and promotes emotional well-being.
- Stimulation: Gentle stimulation through touch, sound, and visual cues supports sensory development.
Parental Involvement and Support
Bonding with Your Preemie
Bonding is essential for both the baby and parents. Strategies to enhance bonding include:
- Kangaroo Care: As mentioned, skin-to-skin contact is beneficial.
- Holding and Touching: Gentle holding and touching, as guided by the NICU staff.
- Feeding and Care: Participating in feeding and daily care routines.
Emotional Support for Parents
Caring for a preemie can be emotionally challenging. Parents should:
- Seek Support: Join support groups for parents of preemies.
- Counseling: Consider professional counseling to manage stress and anxiety.
- Self-Care: Prioritize self-care to maintain physical and emotional health.
Bringing Your Preemie Home
Preparing the Home Environment
Before bringing your preemie home, ensure the environment is safe and supportive:
- Clean and Hygienic: Maintain a clean environment to reduce infection risk.
- Temperature Control: Keep the home at a comfortable temperature.
- Baby Gear: Ensure that cribs, car seats, and other baby gear are appropriate for a preemie’s size and needs.
Regular Medical Follow-ups
Regular medical follow-ups are crucial to monitor your preemie’s growth and development:
- Pediatric Appointments: Schedule frequent check-ups to track progress and address any concerns.
- Specialist Visits: Depending on health issues, visits to specialists such as neurologists, cardiologists, or ophthalmologists may be necessary.
- Immunizations: Follow the recommended immunization schedule to protect against infections.
Conclusion
Caring for a preemie requires special considerations and a proactive approach to ensure their health and development. With the right medical care, developmental support, and parental involvement, preemies can thrive and reach their full potential. By understanding their unique needs and challenges, parents can provide a safe, nurturing environment that supports their baby’s growth and well-being. Remember, every preemie’s journey is unique, and with patience, love, and care, you can navigate this journey successfully.