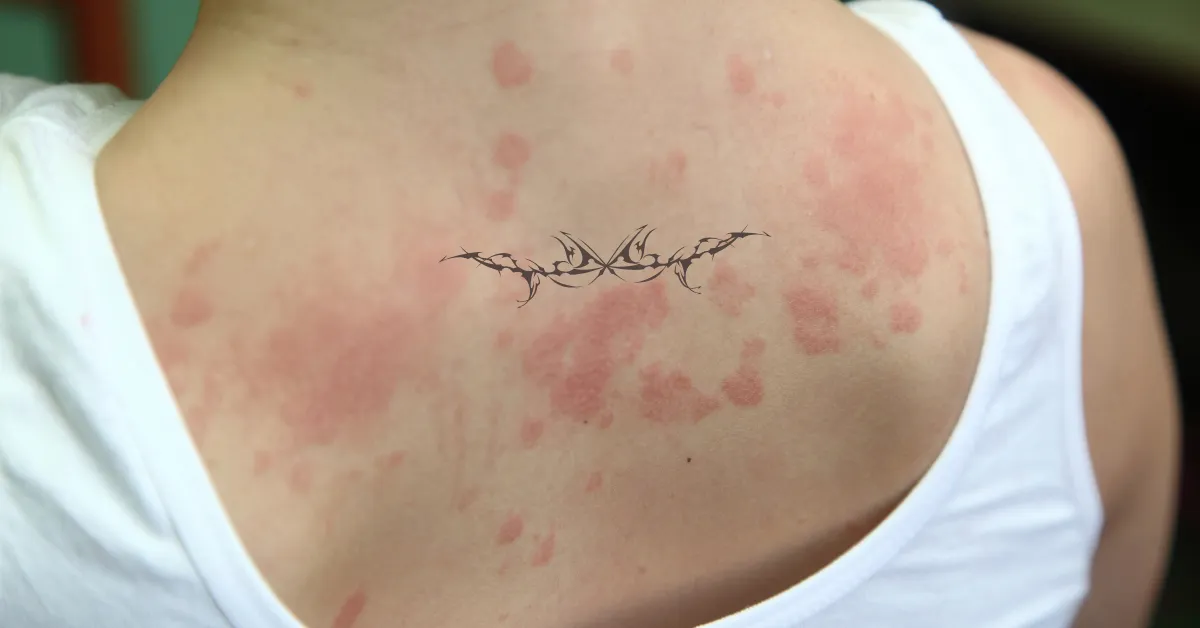
While tattoos are traditionally associated with adults, temporary tattoos, henna, or ink designs are increasingly popular among children. However, these tattoos can pose risks, including allergic reactions to the ink. This article explores the potential allergies, symptoms, causes, prevention, and treatment of tattoo-related reactions in children.
What Are Ink Tattoos and How Do They Affect Children?
Ink Tattoos refer to designs created on the skin using permanent or temporary ink. While permanent tattoos involve inserting pigments into the dermis layer of the skin, temporary tattoos use surface-level applications like stickers or henna.
Children’s skin is more sensitive than adults’, making them more prone to allergies or irritation from tattoo inks, adhesives, or dyes.
Common Allergic Reactions to Ink Tattoos
1. Contact Dermatitis
• Symptoms: Redness, itching, swelling, or rashes around the tattooed area.
• Cause: Hypersensitivity to ingredients in tattoo ink or adhesives in temporary tattoos.
2. Chemical Sensitivity
• Symptoms: Burning sensation, blisters, or peeling skin.
• Cause: Reaction to harsh chemicals in certain dyes, particularly in black henna or metallic inks.
3. Photoallergic Reaction
• Symptoms: Itchy or swollen skin triggered by sunlight exposure.
• Cause: Interaction of tattoo ink chemicals with UV rays.
4. Severe Allergies (Rare)
• Symptoms: Breathing difficulties, widespread hives, or anaphylaxis.
• Cause: Hypersensitivity to specific compounds like paraphenylenediamine (PPD) in henna or heavy metals in inks.
Causes of Tattoo-Related Allergies in Children
1. Chemical Additives in Ink
• Temporary Tattoos: Adhesives or dyes containing synthetic fragrances, parabens, or PPD.
• Permanent Tattoos: Heavy metals like mercury, lead, or chromium used as colorants.
2. Natural Allergens
• Even natural henna can cause irritation due to plant-derived allergens.
3. Improper Application
• Tattoos applied with contaminated tools or low-quality ink increase the risk of allergic reactions and infections.
4. Underlying Skin Conditions
• Children with eczema, psoriasis, or sensitive skin are more prone to adverse reactions.
Symptoms of Tattoo-Related Allergies in Children
• Redness and swelling around the tattooed area
• Persistent itching or burning
• Raised or blistered skin (may look like hives)
• Flaking or peeling skin
• Pain or discomfort at the site
• Severe cases: Systemic symptoms like fever or difficulty breathing
Prevention of Allergic Reactions to Tattoos
1. Choose Safe Products
• Use hypoallergenic or dermatologist-tested temporary tattoos for children.
• Avoid black henna, which often contains high levels of PPD.
2. Patch Testing
• Perform a patch test by applying a small amount of tattoo ink or adhesive to the skin and monitoring for 24–48 hours.
3. Educate Children
• Teach children not to scratch or pick at tattoos to reduce irritation or infection risks.
4. Avoid Sun Exposure
• Protect tattooed skin from direct sunlight to prevent photoallergic reactions.
5. Limit Age-Inappropriate Tattoos
• Permanent tattoos are not suitable for children due to health and ethical concerns.
If an Allergic Reaction Occurs
1. Mild Reactions
• Clean the Area: Gently wash with mild soap and water.
• Apply a Cool Compress: Reduces swelling and discomfort.
• Use Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream or antihistamine ointments can help alleviate itching and inflammation.
2. Moderate Reactions
• Administer oral antihistamines like cetirizine or loratadine (after consulting a doctor).
• Monitor the child for worsening symptoms.
3. Severe Reactions
• If symptoms like difficulty breathing, extensive swelling, or systemic hives occur, seek immediate medical attention.
• Anaphylactic reactions may require emergency treatment, including epinephrine injection.
When to See a Doctor
• Persistent redness or swelling lasting more than 48 hours
• Development of blisters, pus, or signs of infection
• Fever or other systemic symptoms
• Any severe allergic reaction
Treatment Options for Allergic Reactions
1. Topical Treatments
• Hydrocortisone creams or calamine lotion to soothe mild rashes.
2. Oral Medications
• Antihistamines for allergic reactions.
• Antibiotics if a secondary bacterial infection develops.
3. Specialized Care
• Dermatologist consultation for severe or recurring reactions.
• Allergy testing to identify specific triggers.
Conclusion
While temporary tattoos can be a fun activity for children, they may pose risks of allergic reactions due to the sensitivity of their skin. Parents should prioritize safe products, perform patch tests, and closely monitor any symptoms after application. In case of an allergic reaction, prompt care and treatment are essential. By taking preventive measures, children can enjoy tattoos safely and without complications.
References
• American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD). Temporary tattoo safety tips.
• Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Tattoo inks and allergic reactions.
• National Eczema Association. Understanding skin sensitivities in children.